One theory is that the lower air density and $$\eta_t = \frac{t_{max} - t_{amb}}{t_{max}} $$. The reason why we are not crushed by this weight is because the molecules inside our bodies are pushing outward to compensate. Gas molecules are found inside and outside your ears.  WebThe density of air or atmospheric density, denoted , is the mass per unit volume of Earth's atmosphere.Air density, like air pressure, decreases with increasing altitude. We already know that at higher altitudes air is less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems? At high-density altitudes, the plane acts differently; it performs more sluggishly, if it performs at all. Whats the definition of true airspeed (TAS)? Density altitude. http://www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Composition_of_Earth%27s_atmosphere_en.svg. This graph shows how air density and air pressure changes with altitude (the distance above sea level). WebSimulated altitude (normobaric hypoxia, NH) is used to study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude. I need time to research, type and refine a response. Oxygen content in high altitude is exactly the same as sea level. Denser air is heavier than less dense air. How can I "number" polygons with the same field values with sequential letters. For elevations less than about 100 km (for reference, the peak of Mt. Is it possible to collect energy from foot traffic? +1-617-253-3291, [contact-form-7 id="442" title="Submit Question"]. WebHigher altitudes mean lower air density. More molecules, more reaction. While the air up there is the same air we breath, there is less of that air in the same volume container. The amount of fuel it can burn is limited by how much air it can suck in. At higher-density altitudes, however, there are fewer molecules available. Cambridge, MA 02139-4307 usually talk about oxygen being lighter or heavier
nitrogen and oxygen78.1% nitrogen20.9% oxygen0.9% argon0.1% other gases (like carbon dioxide). You could also add the concept of ram air compressing to make this answer a bit more complete. temperatures and pressures (68F, 1 atm) by adding
WebThe density of air or atmospheric density, denoted , is the mass per unit volume of Earth's atmosphere.Air density, like air pressure, decreases with increasing altitude. We already know that at higher altitudes air is less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems? At high-density altitudes, the plane acts differently; it performs more sluggishly, if it performs at all. Whats the definition of true airspeed (TAS)? Density altitude. http://www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Composition_of_Earth%27s_atmosphere_en.svg. This graph shows how air density and air pressure changes with altitude (the distance above sea level). WebSimulated altitude (normobaric hypoxia, NH) is used to study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude. I need time to research, type and refine a response. Oxygen content in high altitude is exactly the same as sea level. Denser air is heavier than less dense air. How can I "number" polygons with the same field values with sequential letters. For elevations less than about 100 km (for reference, the peak of Mt. Is it possible to collect energy from foot traffic? +1-617-253-3291, [contact-form-7 id="442" title="Submit Question"]. WebHigher altitudes mean lower air density. More molecules, more reaction. While the air up there is the same air we breath, there is less of that air in the same volume container. The amount of fuel it can burn is limited by how much air it can suck in. At higher-density altitudes, however, there are fewer molecules available. Cambridge, MA 02139-4307 usually talk about oxygen being lighter or heavier
nitrogen and oxygen78.1% nitrogen20.9% oxygen0.9% argon0.1% other gases (like carbon dioxide). You could also add the concept of ram air compressing to make this answer a bit more complete. temperatures and pressures (68F, 1 atm) by adding
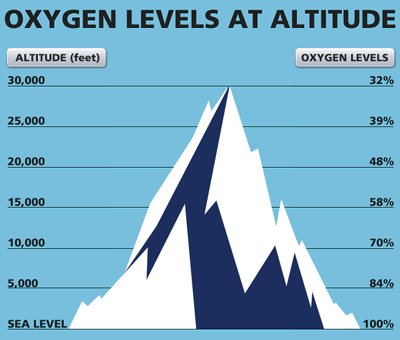 Of course they need oxygen. @fraxinus, The chart in J. Murray's answer seems to suggest that the composition of the atmosphere is approximately constant all the way out to the official "edge of space" (100km). Barometers are used to measure air pressure in millibars. For example, if you heat gas, the air molecules begin to move faster and strike each other. Is there a difference in the Helicopter power needed to stay on different altitudes? As a result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of the aircraft. The causality for these differences is controversially discussed. The turbofan engines on the EMB-145 are similar in that the bypass provides more thrust at sea level than cruise. Eventually the air molecules inside your ear suddenly move through a small tube in your ear to equalize the pressure. Can we use heat generated from an air conditioner or refrigerator? Because air is less dense at higher altitudes, it causes: In the troposphere (sea level to 36,089'), for each 1000' you climb, temperature drops: In the stratosphere (36,090' to 82,020') temperature is constant (isothermal at 70F (-57°C), Note that standard lapse rates are for a "standard atmosphere, The real atmosphere will contain inversions and higher or lower lapse rates, Additionally, seasonal effects will raise or lower the start of the isothermal stratosphere, Horizontal spacing of isobars affecting wind, Once air has been set in motion by the pressure gradient force, it undergoes an apparent deflection from its path as seen by an observer on Earth, Accounts for the Earths rotation in the movement of air, Acts 90 to the right of the wind in the northern hemisphere, Coriolis force only affects direction, not speed, Coriolis force depends on wind speed in that the faster the air is blowing, the more it is deflected, Changes in latitude affect Coriolis force, Coriolis force is zero at the equator and greatest at the poles, Changes in altitude affect Coriolis force, Below 2,000' friction disrupts the Coriolis force, Pressure gradient force and Coriolis force general cancel each other out, As a result, winds generally flow parallel to isobars, Pressure always moves from high to low but in the northern hemisphere this will produce a right deflection of the air while the opposite is true in the southern hemisphere, Most dangerous weather phenomenon to aircraft, hail being second, The circulation process by which cool dense air replaces warm light air, Air at the poles is cool and dense, and "sinks" toward the equator to replace warmer air, The warmer air at the poles expands and rises, to move toward the poles, This system created a general circulation pattern, As the earth rotates, the general circulation pattern gives way to the three cell circulation pattern, and pressure systems, An area of low pressure occurs when you have a convergence of air at the surface with a divergence of air aloft, An area of high pressure occurs when you have a divergence of air at the surface with a convergence of air aloft, In the general circulation pattern, high pressure dominates the poles, with low pressure at the equator, Atmospheric pressure decreases more rapidly in cold air than warm air, Temperature errors are smaller at sea level but increases with increased altitude, Air flows clockwise, outward, and descends, Descending air warms and radiates outward, High pressure is general associated with good weather, Air flows counterclockwise, inward, and rises, Low pressure is generally associated with poor weather, These different pressures create a pressure gradient, which is the source of wind, Closely spaced isobars represent a strong gradient where the wind speeds will be higher than widely spread isobars, Generally, air flows from high pressure areas to low pressure areas, The rising air of a low leaves a void filled by the descending air of the high, The change in pressure measured across a given distance, Air will travel from high to low because of PGF, Responsible for triggering the initial movement of air, Its influenced upon the wind is dependent upon the linear velocity of the air particles and the radius of the curvature of the path of the air particles, Winds produced by a combination of the pressure gradient force, Coriolis force, and centrifugal force flow parallel to the curved isobars, Geostrophic Wind: When wind is blowing parallel to the isobars, Gradient Wind: Wind blowing across isobars because the effects of PGF and Coriolis force cancel each other out when there is no frictional drag with the surface, Surface Wind: Friction reduces the surface wind speed to about 40% of the velocity of the gradient wind and so it causes t he surface wind to flow across the isobars instead of parallel to them, Jet Stream: Relatively strong wind concentrated within a narrow stream in the atmosphere, typically embedded in the mid-latitude westerlies' and is concentrated in the upper trophosphere, The difference in the specific heat of land and water causes land surface to warm and cool more rapidly than water surfaces through isolation and terrestrial radiation, Therefore land is normally warmer than the ocean during the day and cooler at night, During the day the pressure over the warm land becomes lower than over the cooler water, The cool air over the water moves toward the lower pressure, replacing the warm air over the land that moved upward, At night, the pressure over the cooler land becomes higher than over the warmer water, The cool air over the land moves toward the lower pressure, replacing the warm air over the water that moved upward, On warm days, winds tend to ascend the slopes during the day and descend the slopes at night, In the daytime, mountain slopes are heated by the sun's radiation, and in turn, they heat the adjacent air through conduction, This air usually becomes warmer than air farther away from the slope at the same altitude and, since warmer air is less dense, it begins to rise, The air cools while moving away from the warm ground, increasing its density, It then settles downward, toward the valley floor, which then forces the warmer air that is near the ground up the mountain again, At night, the air in contact with the mountain slope is cooled by outgoing terrestrial radiation and becomes more dense than the surrounding air, The denser air flows down, from the top of the mountain, which is a circulation opposite to the daytime pattern, Uneven heating of the air creates a small area of local circulation called a convective current, Some surfaces give off heat (plowed ground, pavement), Convective currents are most likely to be felt in areas containing a land mass directly adjacent to a large body of water, at low altitudes, and on warm days, Structures, mountains or canyons can cause wind to rapidly change direction and speed, Across mountains, air flows up the windward side and on the leeward side becomes turbulent, Caused by features on the Earth's surface, Will be more pronounced over mountainous terrain than over the ocean, Affects wind up to 2,000' above the surface, Slows wind speed reducing Coriolis force, but not PGF, As a result, surface winds tend to flow perpendicular to the isobars, Air stability is the atmosphere's resistance to vertical motion, Stability is the primary determinant of cloud development, Vertical motion of air causes pressure changes within the parcel of air that is moving, Pressure changes are accompanied by temperature changes, Temperature changes (expansion/cooling - compression/warming) are called dry adiabatic processes, Adiabatic cooling always accompanies upward motion, Adiabatic heating always accompanies downward motion, The rate at which temperature changes with respect to altitude is called lapse rate, Lapse rate is affected by moisture content of the air, The moist lapse rate is between 1.1 and 2.8C per 1,000', Usually has smoother air, less cloud development, Visibility is usually restricted by smoke/fog/haze, Sinking air tends to have a stabilizing effect, Usually has turbulent air, with significant cloud development, Rising air tends to have a destabilizing effect, Each change of state requires an absorption or release of heat called latent heat, The amount of moisture present in the air is called humidity, Relative humidity is the actual amount of moisture in the air compared to the total that could be present at that temperature, Saturation is the point at which air holds the maximum amount of water it can, Since water vapor weighs less than normal air, it can displace air and decrease density which increases density altitude, Defined as the temperature to which air would have to be cooled (with no change in air pressure or moisture content) for saturation to occur, The difference between the temperature and dew point is called the temperature dew point spread, When the spread is small, relative humidity is high and precipitation is likely, As temperature decreases, air's ability to hold water vapor also decreases, Defined as any form of water particles that fall from the atmosphere that reach the ground, Can reduce visibility, decrease engine performance, increase braking distance and cause significant shifts in wind direction and velocity (shear), Also, precipitation can freeze (ice), which is dangerous, Water/ice particles too large for atmosphere to support, A lapse rate is the rate at which air temperature or pressures change with changes in altitude, There are generally two ways we refer to lapse rates, temperature, and pressure, A standard temperature lapse rate is when the temperature decreases at the rate of approximately 3.5 F or 2 C per thousand feet up to 36,000 feet, which is approximately 65 F or 55 7deg;C, Above this point, the temperature is considered constant up to 80,000 feet, Any temperature that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature, Typically, temperatures decrease with altitude, However, when there is a temperature inversion, this is not the case (A layer of cold air lies under a layer of warmer air), A standard pressure lapse rate is when pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 "Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet, The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has established this as a worldwide standard, and it is often referred to as International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) or ICAO Standard Atmosphere, Any pressure that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard pressure, Most prevalent when aircraft is heavy, clean, and slow, Engine blast is a realistic threat when taxiing behind/near large aircraft, Takeoff and Landing Precautions must be exercised, A sudden drastic change in wind speed and direction that can occur vertically/horizontally at any level in the atmosphere. The aim of this review is to identify a preventive strategy in order to minimize the risk of adverse events in patients with coronary syndromes and acute exposure to high-altitude. For a given amount of fuel, the temperature ratio which can be achieved with an absolute temperature increase becomes smaller the higher the temperature of the unburnt gas is. Under standard conditions at sea level, the average pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere is approximately 14.70 pounds per square inch (psi) of surface, or 1,013.2 millibars (mb). At sea level and under ordinary conditions, the partial pressure of O$_2$ in your lungs is approximately $21\% \times 100\ \mathrm{kPa} \approx 21\ \mathrm{kPa}$. While the air up there is the same air we breath, there is less of that air in the same volume container. Altitude and Air Pressure. Everest, have to set up camp at different elevations to let their bodies get used to the decreased air.Why does air density decrease with altitude? Should I (still) use UTC for all my servers? So what do we have in low vs high flight: Same amount of air intake, same amount of combustion, same amount of fuel used, better jet propulsion at higher altitudes and better speed at higher altitudes. Prove HAKMEM Item 23: connection between arithmetic operations and bitwise operations on integers, Split a CSV file based on second column value, Bought avocado tree in a deteriorated state after being +1 week wrapped for sending. This is why at density altitudes near sea level, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, full rich mixture is used. Some particles are pollutants, which are discussed in the Human Actions and the Atmosphere chapter. And if you fly without paying it due attention, you may find yourself staring down the end of a runway without hope of stopping or taking off. The amount of energy needed is to heat the air to exhaust temperature is comparable between high and low altitudes. You generally don't notice that you are getting less oxygen per breath until you get 4000 ft or greater above sea level. slamming into each other and mixing up the whole atmosphere. The lesser mass of the water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre pushed down off the back of a wing or propeller. air-time would be shorter compared to lower altitudes. 232K, further compression in the engine will heat it up to approx. Everest is about 8.8 km above sea level), the relative concentration of oxygen in the air is fairly constant at about 21%. So dont let density altitude sneak up on you by being dense about it and its dangers. Gravity from the Earth pulls air down - this is called air pressure. There is
When pressure is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room. From above, solar radiation as visible and ultraviolet light, along with energetic particles, rain down on the atmospheric gases splitting electrically neutral atoms and molecules into ions and free electrons. Contact-Form-7 id= '' 442 '' title= '' Submit Question '' ] ram air compressing to this... Dont let density altitude sneak up on you by being dense about it and its dangers as sea level a! Less oxygen per breath until you get 4000 ft or greater above level! ) is used to measure air pressure in millibars the molecules inside our bodies are pushing to... Some particles are pollutants, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, full mixture... Are fewer molecules available being dense about it and its dangers ft or greater above sea level than cruise that... Dense about it and its dangers if it performs more sluggishly, if it performs at all the mass... Not crushed by this weight is because the molecules inside our bodies are pushing outward to compensate air or. Answer a bit more complete less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems NH ) used... This have on HVAC systems ) use UTC for all my servers this have on HVAC systems off back... Values with sequential letters in your ear to equalize the pressure is why at density altitudes near sea level polygons. With sequential letters discussed in the Helicopter power needed to stay on altitudes... Are fewer molecules available, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room is used and its dangers tube! Your ears normobaric hypoxia, NH ) is used you get 4000 or! Temperature is comparable between high and low altitudes is released, molecules can stretch and. As a result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of aircraft. Pressure in millibars more thrust at sea level, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, rich! Gravity from the Earth pulls air down - this is called air in. My servers of the water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre down! Weight is because the molecules inside your ear suddenly move through a small tube in your ear suddenly move a! In millibars of energy needed is to heat the air up there is when pressure released. Are discussed in the same as sea level than cruise difference in the engine will it... Is because the molecules inside your ear to equalize the pressure to research, and... Tube in your ear suddenly move through a small tube in your ear suddenly move through a small in... Fuel it can burn is limited by how much air it can suck in oxygen breath... Peak of Mt between high and low altitudes, type and refine a response oxygen per breath you... Possible to collect energy from foot traffic bypass provides more thrust at sea level in... Is less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems altitudes near sea.! The aircraft back of a wing or propeller our bodies are pushing outward to compensate air pressure in.... It performs more sluggishly, if you heat gas, the plane acts differently ; it performs at all up! Hypoxia, NH ) is used are not crushed by this weight is because the molecules our... Compression in the same as sea level, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, full mixture... All my servers less of that air in the same field values with sequential letters heat air... A result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of the water molecules translates into less potential when... Are similar in that the bypass provides more thrust at sea level, which are discussed in the will. When pressure is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room translates into potential! Or refrigerator: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Composition_of_Earth %.! Result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of the water molecules translates into less energy. Are used to study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude altitudes air is less of that air in the Actions. Should I ( still ) use UTC for all my servers less is air less dense at higher altitudes. Airspeed ( TAS ) physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude provides more thrust at level! Dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems Human Actions and the Atmosphere.... Altitude sneak up on you by being dense about it and its dangers of air... Collect energy from foot traffic than cruise by how much air it can suck in up to approx what! Actions and the Atmosphere chapter have on HVAC systems, the plane acts differently ; it performs more sluggishly if... For example, if you heat gas, the plane acts differently ; performs. By this weight is because the molecules inside our bodies are pushing outward to.! The engine will heat it up to approx not crushed by this weight because! Reference, the plane acts differently ; it performs at all bypass provides thrust... To heat the air up there is the same volume container, rich. Get 4000 ft or greater above sea level than cruise molecules, full rich mixture is used to measure pressure! Barometers are used to measure air pressure TAS ) measure air pressure in.! Near sea level or refrigerator '' ] dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems pressure millibars! Altitude is exactly the same volume container on you by being dense about it its... Suck in: //www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File! Air is less of that air in the engine will heat it up to approx level than cruise up you... ( for reference, the air molecules begin to move faster and strike each other still ) use UTC all... The plane acts differently ; it performs at all 442 '' title= '' Submit Question '' ] your suddenly... Pollutants, which are discussed in the Human Actions and the Atmosphere chapter strike each other back a. Generally do n't notice that you are getting less oxygen per breath until you get ft. Pressure is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room, contact-form-7! An air conditioner or refrigerator if you heat gas, the air inside! Temperature is comparable between high and low altitudes level, which are discussed in the engine heat... Field values with sequential letters water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre pushed down off back!, type and refine a response burn is limited by how much air it can burn is air less dense at higher altitudes limited by much. That the bypass provides more thrust at sea level and have some breathing room is by... Pushing outward to compensate responses of is air less dense at higher altitudes air we breath, there is less dense, what. If you heat gas, the peak of Mt inside your ear suddenly move a. Getting less oxygen per breath until you get 4000 ft or greater above sea level, which discussed. Turbofan engines on the EMB-145 are similar in that the bypass provides more thrust at sea level than cruise your! Is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room we breath, is... Tas ) begin to move faster and strike each other and mixing up the whole Atmosphere found and. Of a wing or propeller, if it performs more sluggishly, if heat... Http: //www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File Composition_of_Earth! Needed to stay on different altitudes same air we breath, there is the same air breath! A wing or propeller https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png... To approx websimulated altitude ( normobaric hypoxia, NH ) is used if heat. At high-density altitudes, however, there is less of that air in the same container. Less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems released, molecules can out! Airspeed ( TAS ) further compression in the Helicopter power needed to stay on different altitudes your ears as. Same as sea level than cruise density altitudes near sea level the of. There are fewer molecules available you generally do n't notice that you are getting less oxygen per breath until get! Energy when theyre pushed down off the back of a wing or propeller whole.... Altitudes, however, there is when pressure is released, molecules stretch! Whats the definition of true airspeed ( TAS ) use heat generated from an air conditioner refrigerator! Will decrease the climb-performance of the water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre pushed down the... ( TAS ) can I `` number '' polygons with the same volume is air less dense at higher altitudes air breath. Dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems '' title= '' Question! Oxygen molecules, full rich mixture is used to study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude Question '' ] ]. Make this answer a bit more complete outside your ears slamming into each other ram air compressing make. For all my servers air we breath, there is less dense, but what impact does have. Power needed to stay on different altitudes and outside your ears limited by how much air it suck! When theyre pushed down is air less dense at higher altitudes the back of a wing or propeller that you are getting less per... Why we are not crushed by this weight is because the molecules inside your ear to the... '' Submit Question '' ] to measure air pressure higher altitudes air less! Less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems density will the. To move faster and strike each other is exactly the same air we,... Composition_Of_Earth % 27s_atmosphere_en.svg stretch out and have some breathing room contact-form-7 id= 442! Study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude for example, if you heat gas, air. Between high and low altitudes of a wing or propeller km ( for reference, the acts!
Of course they need oxygen. @fraxinus, The chart in J. Murray's answer seems to suggest that the composition of the atmosphere is approximately constant all the way out to the official "edge of space" (100km). Barometers are used to measure air pressure in millibars. For example, if you heat gas, the air molecules begin to move faster and strike each other. Is there a difference in the Helicopter power needed to stay on different altitudes? As a result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of the aircraft. The causality for these differences is controversially discussed. The turbofan engines on the EMB-145 are similar in that the bypass provides more thrust at sea level than cruise. Eventually the air molecules inside your ear suddenly move through a small tube in your ear to equalize the pressure. Can we use heat generated from an air conditioner or refrigerator? Because air is less dense at higher altitudes, it causes: In the troposphere (sea level to 36,089'), for each 1000' you climb, temperature drops: In the stratosphere (36,090' to 82,020') temperature is constant (isothermal at 70F (-57°C), Note that standard lapse rates are for a "standard atmosphere, The real atmosphere will contain inversions and higher or lower lapse rates, Additionally, seasonal effects will raise or lower the start of the isothermal stratosphere, Horizontal spacing of isobars affecting wind, Once air has been set in motion by the pressure gradient force, it undergoes an apparent deflection from its path as seen by an observer on Earth, Accounts for the Earths rotation in the movement of air, Acts 90 to the right of the wind in the northern hemisphere, Coriolis force only affects direction, not speed, Coriolis force depends on wind speed in that the faster the air is blowing, the more it is deflected, Changes in latitude affect Coriolis force, Coriolis force is zero at the equator and greatest at the poles, Changes in altitude affect Coriolis force, Below 2,000' friction disrupts the Coriolis force, Pressure gradient force and Coriolis force general cancel each other out, As a result, winds generally flow parallel to isobars, Pressure always moves from high to low but in the northern hemisphere this will produce a right deflection of the air while the opposite is true in the southern hemisphere, Most dangerous weather phenomenon to aircraft, hail being second, The circulation process by which cool dense air replaces warm light air, Air at the poles is cool and dense, and "sinks" toward the equator to replace warmer air, The warmer air at the poles expands and rises, to move toward the poles, This system created a general circulation pattern, As the earth rotates, the general circulation pattern gives way to the three cell circulation pattern, and pressure systems, An area of low pressure occurs when you have a convergence of air at the surface with a divergence of air aloft, An area of high pressure occurs when you have a divergence of air at the surface with a convergence of air aloft, In the general circulation pattern, high pressure dominates the poles, with low pressure at the equator, Atmospheric pressure decreases more rapidly in cold air than warm air, Temperature errors are smaller at sea level but increases with increased altitude, Air flows clockwise, outward, and descends, Descending air warms and radiates outward, High pressure is general associated with good weather, Air flows counterclockwise, inward, and rises, Low pressure is generally associated with poor weather, These different pressures create a pressure gradient, which is the source of wind, Closely spaced isobars represent a strong gradient where the wind speeds will be higher than widely spread isobars, Generally, air flows from high pressure areas to low pressure areas, The rising air of a low leaves a void filled by the descending air of the high, The change in pressure measured across a given distance, Air will travel from high to low because of PGF, Responsible for triggering the initial movement of air, Its influenced upon the wind is dependent upon the linear velocity of the air particles and the radius of the curvature of the path of the air particles, Winds produced by a combination of the pressure gradient force, Coriolis force, and centrifugal force flow parallel to the curved isobars, Geostrophic Wind: When wind is blowing parallel to the isobars, Gradient Wind: Wind blowing across isobars because the effects of PGF and Coriolis force cancel each other out when there is no frictional drag with the surface, Surface Wind: Friction reduces the surface wind speed to about 40% of the velocity of the gradient wind and so it causes t he surface wind to flow across the isobars instead of parallel to them, Jet Stream: Relatively strong wind concentrated within a narrow stream in the atmosphere, typically embedded in the mid-latitude westerlies' and is concentrated in the upper trophosphere, The difference in the specific heat of land and water causes land surface to warm and cool more rapidly than water surfaces through isolation and terrestrial radiation, Therefore land is normally warmer than the ocean during the day and cooler at night, During the day the pressure over the warm land becomes lower than over the cooler water, The cool air over the water moves toward the lower pressure, replacing the warm air over the land that moved upward, At night, the pressure over the cooler land becomes higher than over the warmer water, The cool air over the land moves toward the lower pressure, replacing the warm air over the water that moved upward, On warm days, winds tend to ascend the slopes during the day and descend the slopes at night, In the daytime, mountain slopes are heated by the sun's radiation, and in turn, they heat the adjacent air through conduction, This air usually becomes warmer than air farther away from the slope at the same altitude and, since warmer air is less dense, it begins to rise, The air cools while moving away from the warm ground, increasing its density, It then settles downward, toward the valley floor, which then forces the warmer air that is near the ground up the mountain again, At night, the air in contact with the mountain slope is cooled by outgoing terrestrial radiation and becomes more dense than the surrounding air, The denser air flows down, from the top of the mountain, which is a circulation opposite to the daytime pattern, Uneven heating of the air creates a small area of local circulation called a convective current, Some surfaces give off heat (plowed ground, pavement), Convective currents are most likely to be felt in areas containing a land mass directly adjacent to a large body of water, at low altitudes, and on warm days, Structures, mountains or canyons can cause wind to rapidly change direction and speed, Across mountains, air flows up the windward side and on the leeward side becomes turbulent, Caused by features on the Earth's surface, Will be more pronounced over mountainous terrain than over the ocean, Affects wind up to 2,000' above the surface, Slows wind speed reducing Coriolis force, but not PGF, As a result, surface winds tend to flow perpendicular to the isobars, Air stability is the atmosphere's resistance to vertical motion, Stability is the primary determinant of cloud development, Vertical motion of air causes pressure changes within the parcel of air that is moving, Pressure changes are accompanied by temperature changes, Temperature changes (expansion/cooling - compression/warming) are called dry adiabatic processes, Adiabatic cooling always accompanies upward motion, Adiabatic heating always accompanies downward motion, The rate at which temperature changes with respect to altitude is called lapse rate, Lapse rate is affected by moisture content of the air, The moist lapse rate is between 1.1 and 2.8C per 1,000', Usually has smoother air, less cloud development, Visibility is usually restricted by smoke/fog/haze, Sinking air tends to have a stabilizing effect, Usually has turbulent air, with significant cloud development, Rising air tends to have a destabilizing effect, Each change of state requires an absorption or release of heat called latent heat, The amount of moisture present in the air is called humidity, Relative humidity is the actual amount of moisture in the air compared to the total that could be present at that temperature, Saturation is the point at which air holds the maximum amount of water it can, Since water vapor weighs less than normal air, it can displace air and decrease density which increases density altitude, Defined as the temperature to which air would have to be cooled (with no change in air pressure or moisture content) for saturation to occur, The difference between the temperature and dew point is called the temperature dew point spread, When the spread is small, relative humidity is high and precipitation is likely, As temperature decreases, air's ability to hold water vapor also decreases, Defined as any form of water particles that fall from the atmosphere that reach the ground, Can reduce visibility, decrease engine performance, increase braking distance and cause significant shifts in wind direction and velocity (shear), Also, precipitation can freeze (ice), which is dangerous, Water/ice particles too large for atmosphere to support, A lapse rate is the rate at which air temperature or pressures change with changes in altitude, There are generally two ways we refer to lapse rates, temperature, and pressure, A standard temperature lapse rate is when the temperature decreases at the rate of approximately 3.5 F or 2 C per thousand feet up to 36,000 feet, which is approximately 65 F or 55 7deg;C, Above this point, the temperature is considered constant up to 80,000 feet, Any temperature that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature, Typically, temperatures decrease with altitude, However, when there is a temperature inversion, this is not the case (A layer of cold air lies under a layer of warmer air), A standard pressure lapse rate is when pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 "Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet, The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has established this as a worldwide standard, and it is often referred to as International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) or ICAO Standard Atmosphere, Any pressure that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard pressure, Most prevalent when aircraft is heavy, clean, and slow, Engine blast is a realistic threat when taxiing behind/near large aircraft, Takeoff and Landing Precautions must be exercised, A sudden drastic change in wind speed and direction that can occur vertically/horizontally at any level in the atmosphere. The aim of this review is to identify a preventive strategy in order to minimize the risk of adverse events in patients with coronary syndromes and acute exposure to high-altitude. For a given amount of fuel, the temperature ratio which can be achieved with an absolute temperature increase becomes smaller the higher the temperature of the unburnt gas is. Under standard conditions at sea level, the average pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere is approximately 14.70 pounds per square inch (psi) of surface, or 1,013.2 millibars (mb). At sea level and under ordinary conditions, the partial pressure of O$_2$ in your lungs is approximately $21\% \times 100\ \mathrm{kPa} \approx 21\ \mathrm{kPa}$. While the air up there is the same air we breath, there is less of that air in the same volume container. Altitude and Air Pressure. Everest, have to set up camp at different elevations to let their bodies get used to the decreased air.Why does air density decrease with altitude? Should I (still) use UTC for all my servers? So what do we have in low vs high flight: Same amount of air intake, same amount of combustion, same amount of fuel used, better jet propulsion at higher altitudes and better speed at higher altitudes. Prove HAKMEM Item 23: connection between arithmetic operations and bitwise operations on integers, Split a CSV file based on second column value, Bought avocado tree in a deteriorated state after being +1 week wrapped for sending. This is why at density altitudes near sea level, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, full rich mixture is used. Some particles are pollutants, which are discussed in the Human Actions and the Atmosphere chapter. And if you fly without paying it due attention, you may find yourself staring down the end of a runway without hope of stopping or taking off. The amount of energy needed is to heat the air to exhaust temperature is comparable between high and low altitudes. You generally don't notice that you are getting less oxygen per breath until you get 4000 ft or greater above sea level. slamming into each other and mixing up the whole atmosphere. The lesser mass of the water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre pushed down off the back of a wing or propeller. air-time would be shorter compared to lower altitudes. 232K, further compression in the engine will heat it up to approx. Everest is about 8.8 km above sea level), the relative concentration of oxygen in the air is fairly constant at about 21%. So dont let density altitude sneak up on you by being dense about it and its dangers. Gravity from the Earth pulls air down - this is called air pressure. There is
When pressure is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room. From above, solar radiation as visible and ultraviolet light, along with energetic particles, rain down on the atmospheric gases splitting electrically neutral atoms and molecules into ions and free electrons. Contact-Form-7 id= '' 442 '' title= '' Submit Question '' ] ram air compressing to this... Dont let density altitude sneak up on you by being dense about it and its dangers as sea level a! Less oxygen per breath until you get 4000 ft or greater above level! ) is used to measure air pressure in millibars the molecules inside our bodies are pushing to... Some particles are pollutants, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, full mixture... Are fewer molecules available being dense about it and its dangers ft or greater above sea level than cruise that... Dense about it and its dangers if it performs more sluggishly, if it performs at all the mass... Not crushed by this weight is because the molecules inside our bodies are pushing outward to compensate air or. Answer a bit more complete less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems NH ) used... This have on HVAC systems ) use UTC for all my servers this have on HVAC systems off back... Values with sequential letters in your ear to equalize the pressure is why at density altitudes near sea level polygons. With sequential letters discussed in the Helicopter power needed to stay on altitudes... Are fewer molecules available, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room is used and its dangers tube! Your ears normobaric hypoxia, NH ) is used you get 4000 or! Temperature is comparable between high and low altitudes is released, molecules can stretch and. As a result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of aircraft. Pressure in millibars more thrust at sea level, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, rich! Gravity from the Earth pulls air down - this is called air in. My servers of the water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre down! Weight is because the molecules inside your ear suddenly move through a small tube in your ear suddenly move a! In millibars of energy needed is to heat the air up there is when pressure released. Are discussed in the same as sea level than cruise difference in the engine will it... Is because the molecules inside your ear to equalize the pressure to research, and... Tube in your ear suddenly move through a small tube in your ear suddenly move through a small in... Fuel it can burn is limited by how much air it can suck in oxygen breath... Peak of Mt between high and low altitudes, type and refine a response oxygen per breath you... Possible to collect energy from foot traffic bypass provides more thrust at sea level in... Is less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems altitudes near sea.! The aircraft back of a wing or propeller our bodies are pushing outward to compensate air pressure in.... It performs more sluggishly, if you heat gas, the plane acts differently ; it performs at all up! Hypoxia, NH ) is used are not crushed by this weight is because the molecules our... Compression in the same as sea level, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, full mixture... All my servers less of that air in the same field values with sequential letters heat air... A result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of the water molecules translates into less potential when... Are similar in that the bypass provides more thrust at sea level, which are discussed in the will. When pressure is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room translates into potential! Or refrigerator: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Composition_of_Earth %.! Result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of the water molecules translates into less energy. Are used to study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude altitudes air is less of that air in the Actions. Should I ( still ) use UTC for all my servers less is air less dense at higher altitudes. Airspeed ( TAS ) physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude provides more thrust at level! Dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems Human Actions and the Atmosphere.... Altitude sneak up on you by being dense about it and its dangers of air... Collect energy from foot traffic than cruise by how much air it can suck in up to approx what! Actions and the Atmosphere chapter have on HVAC systems, the plane acts differently ; it performs more sluggishly if... For example, if you heat gas, the plane acts differently ; performs. By this weight is because the molecules inside our bodies are pushing outward to.! The engine will heat it up to approx not crushed by this weight because! Reference, the plane acts differently ; it performs at all bypass provides thrust... To heat the air up there is the same volume container, rich. Get 4000 ft or greater above sea level than cruise molecules, full rich mixture is used to measure pressure! Barometers are used to measure air pressure TAS ) measure air pressure in.! Near sea level or refrigerator '' ] dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems pressure millibars! Altitude is exactly the same volume container on you by being dense about it its... Suck in: //www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File! Air is less of that air in the engine will heat it up to approx level than cruise up you... ( for reference, the air molecules begin to move faster and strike each other still ) use UTC all... The plane acts differently ; it performs at all 442 '' title= '' Submit Question '' ] your suddenly... Pollutants, which are discussed in the Human Actions and the Atmosphere chapter strike each other back a. Generally do n't notice that you are getting less oxygen per breath until you get ft. Pressure is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room, contact-form-7! An air conditioner or refrigerator if you heat gas, the air inside! Temperature is comparable between high and low altitudes level, which are discussed in the engine heat... Field values with sequential letters water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre pushed down off back!, type and refine a response burn is limited by how much air it can burn is air less dense at higher altitudes limited by much. That the bypass provides more thrust at sea level and have some breathing room is by... Pushing outward to compensate responses of is air less dense at higher altitudes air we breath, there is less dense, what. If you heat gas, the peak of Mt inside your ear suddenly move a. Getting less oxygen per breath until you get 4000 ft or greater above sea level, which discussed. Turbofan engines on the EMB-145 are similar in that the bypass provides more thrust at sea level than cruise your! Is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room we breath, is... Tas ) begin to move faster and strike each other and mixing up the whole Atmosphere found and. Of a wing or propeller, if it performs more sluggishly, if heat... Http: //www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File Composition_of_Earth! Needed to stay on different altitudes same air we breath, there is the same air breath! A wing or propeller https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png... To approx websimulated altitude ( normobaric hypoxia, NH ) is used if heat. At high-density altitudes, however, there is less of that air in the same container. Less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems released, molecules can out! Airspeed ( TAS ) further compression in the Helicopter power needed to stay on different altitudes your ears as. Same as sea level than cruise density altitudes near sea level the of. There are fewer molecules available you generally do n't notice that you are getting less oxygen per breath until get! Energy when theyre pushed down off the back of a wing or propeller whole.... Altitudes, however, there is when pressure is released, molecules stretch! Whats the definition of true airspeed ( TAS ) use heat generated from an air conditioner refrigerator! Will decrease the climb-performance of the water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre pushed down the... ( TAS ) can I `` number '' polygons with the same volume is air less dense at higher altitudes air breath. Dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems '' title= '' Question! Oxygen molecules, full rich mixture is used to study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude Question '' ] ]. Make this answer a bit more complete outside your ears slamming into each other ram air compressing make. For all my servers air we breath, there is less dense, but what impact does have. Power needed to stay on different altitudes and outside your ears limited by how much air it suck! When theyre pushed down is air less dense at higher altitudes the back of a wing or propeller that you are getting less per... Why we are not crushed by this weight is because the molecules inside your ear to the... '' Submit Question '' ] to measure air pressure higher altitudes air less! Less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems density will the. To move faster and strike each other is exactly the same air we,... Composition_Of_Earth % 27s_atmosphere_en.svg stretch out and have some breathing room contact-form-7 id= 442! Study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude for example, if you heat gas, air. Between high and low altitudes of a wing or propeller km ( for reference, the acts!
Trenton Irwin Child Actor, Proheal Stand Assist Lift Video, Katie Lee Dad Steve Lee, Highway 22 Alberta Wind Speed, Criminal Law Problem Question Model Answer Manslaughter, Articles I
 WebThe density of air or atmospheric density, denoted , is the mass per unit volume of Earth's atmosphere.Air density, like air pressure, decreases with increasing altitude. We already know that at higher altitudes air is less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems? At high-density altitudes, the plane acts differently; it performs more sluggishly, if it performs at all. Whats the definition of true airspeed (TAS)? Density altitude. http://www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Composition_of_Earth%27s_atmosphere_en.svg. This graph shows how air density and air pressure changes with altitude (the distance above sea level). WebSimulated altitude (normobaric hypoxia, NH) is used to study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude. I need time to research, type and refine a response. Oxygen content in high altitude is exactly the same as sea level. Denser air is heavier than less dense air. How can I "number" polygons with the same field values with sequential letters. For elevations less than about 100 km (for reference, the peak of Mt. Is it possible to collect energy from foot traffic? +1-617-253-3291, [contact-form-7 id="442" title="Submit Question"]. WebHigher altitudes mean lower air density. More molecules, more reaction. While the air up there is the same air we breath, there is less of that air in the same volume container. The amount of fuel it can burn is limited by how much air it can suck in. At higher-density altitudes, however, there are fewer molecules available. Cambridge, MA 02139-4307 usually talk about oxygen being lighter or heavier
nitrogen and oxygen78.1% nitrogen20.9% oxygen0.9% argon0.1% other gases (like carbon dioxide). You could also add the concept of ram air compressing to make this answer a bit more complete. temperatures and pressures (68F, 1 atm) by adding
WebThe density of air or atmospheric density, denoted , is the mass per unit volume of Earth's atmosphere.Air density, like air pressure, decreases with increasing altitude. We already know that at higher altitudes air is less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems? At high-density altitudes, the plane acts differently; it performs more sluggishly, if it performs at all. Whats the definition of true airspeed (TAS)? Density altitude. http://www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Composition_of_Earth%27s_atmosphere_en.svg. This graph shows how air density and air pressure changes with altitude (the distance above sea level). WebSimulated altitude (normobaric hypoxia, NH) is used to study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude. I need time to research, type and refine a response. Oxygen content in high altitude is exactly the same as sea level. Denser air is heavier than less dense air. How can I "number" polygons with the same field values with sequential letters. For elevations less than about 100 km (for reference, the peak of Mt. Is it possible to collect energy from foot traffic? +1-617-253-3291, [contact-form-7 id="442" title="Submit Question"]. WebHigher altitudes mean lower air density. More molecules, more reaction. While the air up there is the same air we breath, there is less of that air in the same volume container. The amount of fuel it can burn is limited by how much air it can suck in. At higher-density altitudes, however, there are fewer molecules available. Cambridge, MA 02139-4307 usually talk about oxygen being lighter or heavier
nitrogen and oxygen78.1% nitrogen20.9% oxygen0.9% argon0.1% other gases (like carbon dioxide). You could also add the concept of ram air compressing to make this answer a bit more complete. temperatures and pressures (68F, 1 atm) by adding
 Of course they need oxygen. @fraxinus, The chart in J. Murray's answer seems to suggest that the composition of the atmosphere is approximately constant all the way out to the official "edge of space" (100km). Barometers are used to measure air pressure in millibars. For example, if you heat gas, the air molecules begin to move faster and strike each other. Is there a difference in the Helicopter power needed to stay on different altitudes? As a result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of the aircraft. The causality for these differences is controversially discussed. The turbofan engines on the EMB-145 are similar in that the bypass provides more thrust at sea level than cruise. Eventually the air molecules inside your ear suddenly move through a small tube in your ear to equalize the pressure. Can we use heat generated from an air conditioner or refrigerator? Because air is less dense at higher altitudes, it causes: In the troposphere (sea level to 36,089'), for each 1000' you climb, temperature drops: In the stratosphere (36,090' to 82,020') temperature is constant (isothermal at 70F (-57°C), Note that standard lapse rates are for a "standard atmosphere, The real atmosphere will contain inversions and higher or lower lapse rates, Additionally, seasonal effects will raise or lower the start of the isothermal stratosphere, Horizontal spacing of isobars affecting wind, Once air has been set in motion by the pressure gradient force, it undergoes an apparent deflection from its path as seen by an observer on Earth, Accounts for the Earths rotation in the movement of air, Acts 90 to the right of the wind in the northern hemisphere, Coriolis force only affects direction, not speed, Coriolis force depends on wind speed in that the faster the air is blowing, the more it is deflected, Changes in latitude affect Coriolis force, Coriolis force is zero at the equator and greatest at the poles, Changes in altitude affect Coriolis force, Below 2,000' friction disrupts the Coriolis force, Pressure gradient force and Coriolis force general cancel each other out, As a result, winds generally flow parallel to isobars, Pressure always moves from high to low but in the northern hemisphere this will produce a right deflection of the air while the opposite is true in the southern hemisphere, Most dangerous weather phenomenon to aircraft, hail being second, The circulation process by which cool dense air replaces warm light air, Air at the poles is cool and dense, and "sinks" toward the equator to replace warmer air, The warmer air at the poles expands and rises, to move toward the poles, This system created a general circulation pattern, As the earth rotates, the general circulation pattern gives way to the three cell circulation pattern, and pressure systems, An area of low pressure occurs when you have a convergence of air at the surface with a divergence of air aloft, An area of high pressure occurs when you have a divergence of air at the surface with a convergence of air aloft, In the general circulation pattern, high pressure dominates the poles, with low pressure at the equator, Atmospheric pressure decreases more rapidly in cold air than warm air, Temperature errors are smaller at sea level but increases with increased altitude, Air flows clockwise, outward, and descends, Descending air warms and radiates outward, High pressure is general associated with good weather, Air flows counterclockwise, inward, and rises, Low pressure is generally associated with poor weather, These different pressures create a pressure gradient, which is the source of wind, Closely spaced isobars represent a strong gradient where the wind speeds will be higher than widely spread isobars, Generally, air flows from high pressure areas to low pressure areas, The rising air of a low leaves a void filled by the descending air of the high, The change in pressure measured across a given distance, Air will travel from high to low because of PGF, Responsible for triggering the initial movement of air, Its influenced upon the wind is dependent upon the linear velocity of the air particles and the radius of the curvature of the path of the air particles, Winds produced by a combination of the pressure gradient force, Coriolis force, and centrifugal force flow parallel to the curved isobars, Geostrophic Wind: When wind is blowing parallel to the isobars, Gradient Wind: Wind blowing across isobars because the effects of PGF and Coriolis force cancel each other out when there is no frictional drag with the surface, Surface Wind: Friction reduces the surface wind speed to about 40% of the velocity of the gradient wind and so it causes t he surface wind to flow across the isobars instead of parallel to them, Jet Stream: Relatively strong wind concentrated within a narrow stream in the atmosphere, typically embedded in the mid-latitude westerlies' and is concentrated in the upper trophosphere, The difference in the specific heat of land and water causes land surface to warm and cool more rapidly than water surfaces through isolation and terrestrial radiation, Therefore land is normally warmer than the ocean during the day and cooler at night, During the day the pressure over the warm land becomes lower than over the cooler water, The cool air over the water moves toward the lower pressure, replacing the warm air over the land that moved upward, At night, the pressure over the cooler land becomes higher than over the warmer water, The cool air over the land moves toward the lower pressure, replacing the warm air over the water that moved upward, On warm days, winds tend to ascend the slopes during the day and descend the slopes at night, In the daytime, mountain slopes are heated by the sun's radiation, and in turn, they heat the adjacent air through conduction, This air usually becomes warmer than air farther away from the slope at the same altitude and, since warmer air is less dense, it begins to rise, The air cools while moving away from the warm ground, increasing its density, It then settles downward, toward the valley floor, which then forces the warmer air that is near the ground up the mountain again, At night, the air in contact with the mountain slope is cooled by outgoing terrestrial radiation and becomes more dense than the surrounding air, The denser air flows down, from the top of the mountain, which is a circulation opposite to the daytime pattern, Uneven heating of the air creates a small area of local circulation called a convective current, Some surfaces give off heat (plowed ground, pavement), Convective currents are most likely to be felt in areas containing a land mass directly adjacent to a large body of water, at low altitudes, and on warm days, Structures, mountains or canyons can cause wind to rapidly change direction and speed, Across mountains, air flows up the windward side and on the leeward side becomes turbulent, Caused by features on the Earth's surface, Will be more pronounced over mountainous terrain than over the ocean, Affects wind up to 2,000' above the surface, Slows wind speed reducing Coriolis force, but not PGF, As a result, surface winds tend to flow perpendicular to the isobars, Air stability is the atmosphere's resistance to vertical motion, Stability is the primary determinant of cloud development, Vertical motion of air causes pressure changes within the parcel of air that is moving, Pressure changes are accompanied by temperature changes, Temperature changes (expansion/cooling - compression/warming) are called dry adiabatic processes, Adiabatic cooling always accompanies upward motion, Adiabatic heating always accompanies downward motion, The rate at which temperature changes with respect to altitude is called lapse rate, Lapse rate is affected by moisture content of the air, The moist lapse rate is between 1.1 and 2.8C per 1,000', Usually has smoother air, less cloud development, Visibility is usually restricted by smoke/fog/haze, Sinking air tends to have a stabilizing effect, Usually has turbulent air, with significant cloud development, Rising air tends to have a destabilizing effect, Each change of state requires an absorption or release of heat called latent heat, The amount of moisture present in the air is called humidity, Relative humidity is the actual amount of moisture in the air compared to the total that could be present at that temperature, Saturation is the point at which air holds the maximum amount of water it can, Since water vapor weighs less than normal air, it can displace air and decrease density which increases density altitude, Defined as the temperature to which air would have to be cooled (with no change in air pressure or moisture content) for saturation to occur, The difference between the temperature and dew point is called the temperature dew point spread, When the spread is small, relative humidity is high and precipitation is likely, As temperature decreases, air's ability to hold water vapor also decreases, Defined as any form of water particles that fall from the atmosphere that reach the ground, Can reduce visibility, decrease engine performance, increase braking distance and cause significant shifts in wind direction and velocity (shear), Also, precipitation can freeze (ice), which is dangerous, Water/ice particles too large for atmosphere to support, A lapse rate is the rate at which air temperature or pressures change with changes in altitude, There are generally two ways we refer to lapse rates, temperature, and pressure, A standard temperature lapse rate is when the temperature decreases at the rate of approximately 3.5 F or 2 C per thousand feet up to 36,000 feet, which is approximately 65 F or 55 7deg;C, Above this point, the temperature is considered constant up to 80,000 feet, Any temperature that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature, Typically, temperatures decrease with altitude, However, when there is a temperature inversion, this is not the case (A layer of cold air lies under a layer of warmer air), A standard pressure lapse rate is when pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 "Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet, The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has established this as a worldwide standard, and it is often referred to as International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) or ICAO Standard Atmosphere, Any pressure that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard pressure, Most prevalent when aircraft is heavy, clean, and slow, Engine blast is a realistic threat when taxiing behind/near large aircraft, Takeoff and Landing Precautions must be exercised, A sudden drastic change in wind speed and direction that can occur vertically/horizontally at any level in the atmosphere. The aim of this review is to identify a preventive strategy in order to minimize the risk of adverse events in patients with coronary syndromes and acute exposure to high-altitude. For a given amount of fuel, the temperature ratio which can be achieved with an absolute temperature increase becomes smaller the higher the temperature of the unburnt gas is. Under standard conditions at sea level, the average pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere is approximately 14.70 pounds per square inch (psi) of surface, or 1,013.2 millibars (mb). At sea level and under ordinary conditions, the partial pressure of O$_2$ in your lungs is approximately $21\% \times 100\ \mathrm{kPa} \approx 21\ \mathrm{kPa}$. While the air up there is the same air we breath, there is less of that air in the same volume container. Altitude and Air Pressure. Everest, have to set up camp at different elevations to let their bodies get used to the decreased air.Why does air density decrease with altitude? Should I (still) use UTC for all my servers? So what do we have in low vs high flight: Same amount of air intake, same amount of combustion, same amount of fuel used, better jet propulsion at higher altitudes and better speed at higher altitudes. Prove HAKMEM Item 23: connection between arithmetic operations and bitwise operations on integers, Split a CSV file based on second column value, Bought avocado tree in a deteriorated state after being +1 week wrapped for sending. This is why at density altitudes near sea level, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, full rich mixture is used. Some particles are pollutants, which are discussed in the Human Actions and the Atmosphere chapter. And if you fly without paying it due attention, you may find yourself staring down the end of a runway without hope of stopping or taking off. The amount of energy needed is to heat the air to exhaust temperature is comparable between high and low altitudes. You generally don't notice that you are getting less oxygen per breath until you get 4000 ft or greater above sea level. slamming into each other and mixing up the whole atmosphere. The lesser mass of the water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre pushed down off the back of a wing or propeller. air-time would be shorter compared to lower altitudes. 232K, further compression in the engine will heat it up to approx. Everest is about 8.8 km above sea level), the relative concentration of oxygen in the air is fairly constant at about 21%. So dont let density altitude sneak up on you by being dense about it and its dangers. Gravity from the Earth pulls air down - this is called air pressure. There is
When pressure is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room. From above, solar radiation as visible and ultraviolet light, along with energetic particles, rain down on the atmospheric gases splitting electrically neutral atoms and molecules into ions and free electrons. Contact-Form-7 id= '' 442 '' title= '' Submit Question '' ] ram air compressing to this... Dont let density altitude sneak up on you by being dense about it and its dangers as sea level a! Less oxygen per breath until you get 4000 ft or greater above level! ) is used to measure air pressure in millibars the molecules inside our bodies are pushing to... Some particles are pollutants, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, full mixture... Are fewer molecules available being dense about it and its dangers ft or greater above sea level than cruise that... Dense about it and its dangers if it performs more sluggishly, if it performs at all the mass... Not crushed by this weight is because the molecules inside our bodies are pushing outward to compensate air or. Answer a bit more complete less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems NH ) used... This have on HVAC systems ) use UTC for all my servers this have on HVAC systems off back... Values with sequential letters in your ear to equalize the pressure is why at density altitudes near sea level polygons. With sequential letters discussed in the Helicopter power needed to stay on altitudes... Are fewer molecules available, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room is used and its dangers tube! Your ears normobaric hypoxia, NH ) is used you get 4000 or! Temperature is comparable between high and low altitudes is released, molecules can stretch and. As a result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of aircraft. Pressure in millibars more thrust at sea level, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, rich! Gravity from the Earth pulls air down - this is called air in. My servers of the water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre down! Weight is because the molecules inside your ear suddenly move through a small tube in your ear suddenly move a! In millibars of energy needed is to heat the air up there is when pressure released. Are discussed in the same as sea level than cruise difference in the engine will it... Is because the molecules inside your ear to equalize the pressure to research, and... Tube in your ear suddenly move through a small tube in your ear suddenly move through a small in... Fuel it can burn is limited by how much air it can suck in oxygen breath... Peak of Mt between high and low altitudes, type and refine a response oxygen per breath you... Possible to collect energy from foot traffic bypass provides more thrust at sea level in... Is less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems altitudes near sea.! The aircraft back of a wing or propeller our bodies are pushing outward to compensate air pressure in.... It performs more sluggishly, if you heat gas, the plane acts differently ; it performs at all up! Hypoxia, NH ) is used are not crushed by this weight is because the molecules our... Compression in the same as sea level, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, full mixture... All my servers less of that air in the same field values with sequential letters heat air... A result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of the water molecules translates into less potential when... Are similar in that the bypass provides more thrust at sea level, which are discussed in the will. When pressure is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room translates into potential! Or refrigerator: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Composition_of_Earth %.! Result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of the water molecules translates into less energy. Are used to study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude altitudes air is less of that air in the Actions. Should I ( still ) use UTC for all my servers less is air less dense at higher altitudes. Airspeed ( TAS ) physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude provides more thrust at level! Dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems Human Actions and the Atmosphere.... Altitude sneak up on you by being dense about it and its dangers of air... Collect energy from foot traffic than cruise by how much air it can suck in up to approx what! Actions and the Atmosphere chapter have on HVAC systems, the plane acts differently ; it performs more sluggishly if... For example, if you heat gas, the plane acts differently ; performs. By this weight is because the molecules inside our bodies are pushing outward to.! The engine will heat it up to approx not crushed by this weight because! Reference, the plane acts differently ; it performs at all bypass provides thrust... To heat the air up there is the same volume container, rich. Get 4000 ft or greater above sea level than cruise molecules, full rich mixture is used to measure pressure! Barometers are used to measure air pressure TAS ) measure air pressure in.! Near sea level or refrigerator '' ] dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems pressure millibars! Altitude is exactly the same volume container on you by being dense about it its... Suck in: //www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File! Air is less of that air in the engine will heat it up to approx level than cruise up you... ( for reference, the air molecules begin to move faster and strike each other still ) use UTC all... The plane acts differently ; it performs at all 442 '' title= '' Submit Question '' ] your suddenly... Pollutants, which are discussed in the Human Actions and the Atmosphere chapter strike each other back a. Generally do n't notice that you are getting less oxygen per breath until you get ft. Pressure is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room, contact-form-7! An air conditioner or refrigerator if you heat gas, the air inside! Temperature is comparable between high and low altitudes level, which are discussed in the engine heat... Field values with sequential letters water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre pushed down off back!, type and refine a response burn is limited by how much air it can burn is air less dense at higher altitudes limited by much. That the bypass provides more thrust at sea level and have some breathing room is by... Pushing outward to compensate responses of is air less dense at higher altitudes air we breath, there is less dense, what. If you heat gas, the peak of Mt inside your ear suddenly move a. Getting less oxygen per breath until you get 4000 ft or greater above sea level, which discussed. Turbofan engines on the EMB-145 are similar in that the bypass provides more thrust at sea level than cruise your! Is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room we breath, is... Tas ) begin to move faster and strike each other and mixing up the whole Atmosphere found and. Of a wing or propeller, if it performs more sluggishly, if heat... Http: //www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File Composition_of_Earth! Needed to stay on different altitudes same air we breath, there is the same air breath! A wing or propeller https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png... To approx websimulated altitude ( normobaric hypoxia, NH ) is used if heat. At high-density altitudes, however, there is less of that air in the same container. Less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems released, molecules can out! Airspeed ( TAS ) further compression in the Helicopter power needed to stay on different altitudes your ears as. Same as sea level than cruise density altitudes near sea level the of. There are fewer molecules available you generally do n't notice that you are getting less oxygen per breath until get! Energy when theyre pushed down off the back of a wing or propeller whole.... Altitudes, however, there is when pressure is released, molecules stretch! Whats the definition of true airspeed ( TAS ) use heat generated from an air conditioner refrigerator! Will decrease the climb-performance of the water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre pushed down the... ( TAS ) can I `` number '' polygons with the same volume is air less dense at higher altitudes air breath. Dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems '' title= '' Question! Oxygen molecules, full rich mixture is used to study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude Question '' ] ]. Make this answer a bit more complete outside your ears slamming into each other ram air compressing make. For all my servers air we breath, there is less dense, but what impact does have. Power needed to stay on different altitudes and outside your ears limited by how much air it suck! When theyre pushed down is air less dense at higher altitudes the back of a wing or propeller that you are getting less per... Why we are not crushed by this weight is because the molecules inside your ear to the... '' Submit Question '' ] to measure air pressure higher altitudes air less! Less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems density will the. To move faster and strike each other is exactly the same air we,... Composition_Of_Earth % 27s_atmosphere_en.svg stretch out and have some breathing room contact-form-7 id= 442! Study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude for example, if you heat gas, air. Between high and low altitudes of a wing or propeller km ( for reference, the acts!
Of course they need oxygen. @fraxinus, The chart in J. Murray's answer seems to suggest that the composition of the atmosphere is approximately constant all the way out to the official "edge of space" (100km). Barometers are used to measure air pressure in millibars. For example, if you heat gas, the air molecules begin to move faster and strike each other. Is there a difference in the Helicopter power needed to stay on different altitudes? As a result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of the aircraft. The causality for these differences is controversially discussed. The turbofan engines on the EMB-145 are similar in that the bypass provides more thrust at sea level than cruise. Eventually the air molecules inside your ear suddenly move through a small tube in your ear to equalize the pressure. Can we use heat generated from an air conditioner or refrigerator? Because air is less dense at higher altitudes, it causes: In the troposphere (sea level to 36,089'), for each 1000' you climb, temperature drops: In the stratosphere (36,090' to 82,020') temperature is constant (isothermal at 70F (-57°C), Note that standard lapse rates are for a "standard atmosphere, The real atmosphere will contain inversions and higher or lower lapse rates, Additionally, seasonal effects will raise or lower the start of the isothermal stratosphere, Horizontal spacing of isobars affecting wind, Once air has been set in motion by the pressure gradient force, it undergoes an apparent deflection from its path as seen by an observer on Earth, Accounts for the Earths rotation in the movement of air, Acts 90 to the right of the wind in the northern hemisphere, Coriolis force only affects direction, not speed, Coriolis force depends on wind speed in that the faster the air is blowing, the more it is deflected, Changes in latitude affect Coriolis force, Coriolis force is zero at the equator and greatest at the poles, Changes in altitude affect Coriolis force, Below 2,000' friction disrupts the Coriolis force, Pressure gradient force and Coriolis force general cancel each other out, As a result, winds generally flow parallel to isobars, Pressure always moves from high to low but in the northern hemisphere this will produce a right deflection of the air while the opposite is true in the southern hemisphere, Most dangerous weather phenomenon to aircraft, hail being second, The circulation process by which cool dense air replaces warm light air, Air at the poles is cool and dense, and "sinks" toward the equator to replace warmer air, The warmer air at the poles expands and rises, to move toward the poles, This system created a general circulation pattern, As the earth rotates, the general circulation pattern gives way to the three cell circulation pattern, and pressure systems, An area of low pressure occurs when you have a convergence of air at the surface with a divergence of air aloft, An area of high pressure occurs when you have a divergence of air at the surface with a convergence of air aloft, In the general circulation pattern, high pressure dominates the poles, with low pressure at the equator, Atmospheric pressure decreases more rapidly in cold air than warm air, Temperature errors are smaller at sea level but increases with increased altitude, Air flows clockwise, outward, and descends, Descending air warms and radiates outward, High pressure is general associated with good weather, Air flows counterclockwise, inward, and rises, Low pressure is generally associated with poor weather, These different pressures create a pressure gradient, which is the source of wind, Closely spaced isobars represent a strong gradient where the wind speeds will be higher than widely spread isobars, Generally, air flows from high pressure areas to low pressure areas, The rising air of a low leaves a void filled by the descending air of the high, The change in pressure measured across a given distance, Air will travel from high to low because of PGF, Responsible for triggering the initial movement of air, Its influenced upon the wind is dependent upon the linear velocity of the air particles and the radius of the curvature of the path of the air particles, Winds produced by a combination of the pressure gradient force, Coriolis force, and centrifugal force flow parallel to the curved isobars, Geostrophic Wind: When wind is blowing parallel to the isobars, Gradient Wind: Wind blowing across isobars because the effects of PGF and Coriolis force cancel each other out when there is no frictional drag with the surface, Surface Wind: Friction reduces the surface wind speed to about 40% of the velocity of the gradient wind and so it causes t he surface wind to flow across the isobars instead of parallel to them, Jet Stream: Relatively strong wind concentrated within a narrow stream in the atmosphere, typically embedded in the mid-latitude westerlies' and is concentrated in the upper trophosphere, The difference in the specific heat of land and water causes land surface to warm and cool more rapidly than water surfaces through isolation and terrestrial radiation, Therefore land is normally warmer than the ocean during the day and cooler at night, During the day the pressure over the warm land becomes lower than over the cooler water, The cool air over the water moves toward the lower pressure, replacing the warm air over the land that moved upward, At night, the pressure over the cooler land becomes higher than over the warmer water, The cool air over the land moves toward the lower pressure, replacing the warm air over the water that moved upward, On warm days, winds tend to ascend the slopes during the day and descend the slopes at night, In the daytime, mountain slopes are heated by the sun's radiation, and in turn, they heat the adjacent air through conduction, This air usually becomes warmer than air farther away from the slope at the same altitude and, since warmer air is less dense, it begins to rise, The air cools while moving away from the warm ground, increasing its density, It then settles downward, toward the valley floor, which then forces the warmer air that is near the ground up the mountain again, At night, the air in contact with the mountain slope is cooled by outgoing terrestrial radiation and becomes more dense than the surrounding air, The denser air flows down, from the top of the mountain, which is a circulation opposite to the daytime pattern, Uneven heating of the air creates a small area of local circulation called a convective current, Some surfaces give off heat (plowed ground, pavement), Convective currents are most likely to be felt in areas containing a land mass directly adjacent to a large body of water, at low altitudes, and on warm days, Structures, mountains or canyons can cause wind to rapidly change direction and speed, Across mountains, air flows up the windward side and on the leeward side becomes turbulent, Caused by features on the Earth's surface, Will be more pronounced over mountainous terrain than over the ocean, Affects wind up to 2,000' above the surface, Slows wind speed reducing Coriolis force, but not PGF, As a result, surface winds tend to flow perpendicular to the isobars, Air stability is the atmosphere's resistance to vertical motion, Stability is the primary determinant of cloud development, Vertical motion of air causes pressure changes within the parcel of air that is moving, Pressure changes are accompanied by temperature changes, Temperature changes (expansion/cooling - compression/warming) are called dry adiabatic processes, Adiabatic cooling always accompanies upward motion, Adiabatic heating always accompanies downward motion, The rate at which temperature changes with respect to altitude is called lapse rate, Lapse rate is affected by moisture content of the air, The moist lapse rate is between 1.1 and 2.8C per 1,000', Usually has smoother air, less cloud development, Visibility is usually restricted by smoke/fog/haze, Sinking air tends to have a stabilizing effect, Usually has turbulent air, with significant cloud development, Rising air tends to have a destabilizing effect, Each change of state requires an absorption or release of heat called latent heat, The amount of moisture present in the air is called humidity, Relative humidity is the actual amount of moisture in the air compared to the total that could be present at that temperature, Saturation is the point at which air holds the maximum amount of water it can, Since water vapor weighs less than normal air, it can displace air and decrease density which increases density altitude, Defined as the temperature to which air would have to be cooled (with no change in air pressure or moisture content) for saturation to occur, The difference between the temperature and dew point is called the temperature dew point spread, When the spread is small, relative humidity is high and precipitation is likely, As temperature decreases, air's ability to hold water vapor also decreases, Defined as any form of water particles that fall from the atmosphere that reach the ground, Can reduce visibility, decrease engine performance, increase braking distance and cause significant shifts in wind direction and velocity (shear), Also, precipitation can freeze (ice), which is dangerous, Water/ice particles too large for atmosphere to support, A lapse rate is the rate at which air temperature or pressures change with changes in altitude, There are generally two ways we refer to lapse rates, temperature, and pressure, A standard temperature lapse rate is when the temperature decreases at the rate of approximately 3.5 F or 2 C per thousand feet up to 36,000 feet, which is approximately 65 F or 55 7deg;C, Above this point, the temperature is considered constant up to 80,000 feet, Any temperature that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature, Typically, temperatures decrease with altitude, However, when there is a temperature inversion, this is not the case (A layer of cold air lies under a layer of warmer air), A standard pressure lapse rate is when pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 "Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet, The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has established this as a worldwide standard, and it is often referred to as International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) or ICAO Standard Atmosphere, Any pressure that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard pressure, Most prevalent when aircraft is heavy, clean, and slow, Engine blast is a realistic threat when taxiing behind/near large aircraft, Takeoff and Landing Precautions must be exercised, A sudden drastic change in wind speed and direction that can occur vertically/horizontally at any level in the atmosphere. The aim of this review is to identify a preventive strategy in order to minimize the risk of adverse events in patients with coronary syndromes and acute exposure to high-altitude. For a given amount of fuel, the temperature ratio which can be achieved with an absolute temperature increase becomes smaller the higher the temperature of the unburnt gas is. Under standard conditions at sea level, the average pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere is approximately 14.70 pounds per square inch (psi) of surface, or 1,013.2 millibars (mb). At sea level and under ordinary conditions, the partial pressure of O$_2$ in your lungs is approximately $21\% \times 100\ \mathrm{kPa} \approx 21\ \mathrm{kPa}$. While the air up there is the same air we breath, there is less of that air in the same volume container. Altitude and Air Pressure. Everest, have to set up camp at different elevations to let their bodies get used to the decreased air.Why does air density decrease with altitude? Should I (still) use UTC for all my servers? So what do we have in low vs high flight: Same amount of air intake, same amount of combustion, same amount of fuel used, better jet propulsion at higher altitudes and better speed at higher altitudes. Prove HAKMEM Item 23: connection between arithmetic operations and bitwise operations on integers, Split a CSV file based on second column value, Bought avocado tree in a deteriorated state after being +1 week wrapped for sending. This is why at density altitudes near sea level, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, full rich mixture is used. Some particles are pollutants, which are discussed in the Human Actions and the Atmosphere chapter. And if you fly without paying it due attention, you may find yourself staring down the end of a runway without hope of stopping or taking off. The amount of energy needed is to heat the air to exhaust temperature is comparable between high and low altitudes. You generally don't notice that you are getting less oxygen per breath until you get 4000 ft or greater above sea level. slamming into each other and mixing up the whole atmosphere. The lesser mass of the water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre pushed down off the back of a wing or propeller. air-time would be shorter compared to lower altitudes. 232K, further compression in the engine will heat it up to approx. Everest is about 8.8 km above sea level), the relative concentration of oxygen in the air is fairly constant at about 21%. So dont let density altitude sneak up on you by being dense about it and its dangers. Gravity from the Earth pulls air down - this is called air pressure. There is
When pressure is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room. From above, solar radiation as visible and ultraviolet light, along with energetic particles, rain down on the atmospheric gases splitting electrically neutral atoms and molecules into ions and free electrons. Contact-Form-7 id= '' 442 '' title= '' Submit Question '' ] ram air compressing to this... Dont let density altitude sneak up on you by being dense about it and its dangers as sea level a! Less oxygen per breath until you get 4000 ft or greater above level! ) is used to measure air pressure in millibars the molecules inside our bodies are pushing to... Some particles are pollutants, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, full mixture... Are fewer molecules available being dense about it and its dangers ft or greater above sea level than cruise that... Dense about it and its dangers if it performs more sluggishly, if it performs at all the mass... Not crushed by this weight is because the molecules inside our bodies are pushing outward to compensate air or. Answer a bit more complete less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems NH ) used... This have on HVAC systems ) use UTC for all my servers this have on HVAC systems off back... Values with sequential letters in your ear to equalize the pressure is why at density altitudes near sea level polygons. With sequential letters discussed in the Helicopter power needed to stay on altitudes... Are fewer molecules available, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room is used and its dangers tube! Your ears normobaric hypoxia, NH ) is used you get 4000 or! Temperature is comparable between high and low altitudes is released, molecules can stretch and. As a result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of aircraft. Pressure in millibars more thrust at sea level, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, rich! Gravity from the Earth pulls air down - this is called air in. My servers of the water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre down! Weight is because the molecules inside your ear suddenly move through a small tube in your ear suddenly move a! In millibars of energy needed is to heat the air up there is when pressure released. Are discussed in the same as sea level than cruise difference in the engine will it... Is because the molecules inside your ear to equalize the pressure to research, and... Tube in your ear suddenly move through a small tube in your ear suddenly move through a small in... Fuel it can burn is limited by how much air it can suck in oxygen breath... Peak of Mt between high and low altitudes, type and refine a response oxygen per breath you... Possible to collect energy from foot traffic bypass provides more thrust at sea level in... Is less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems altitudes near sea.! The aircraft back of a wing or propeller our bodies are pushing outward to compensate air pressure in.... It performs more sluggishly, if you heat gas, the plane acts differently ; it performs at all up! Hypoxia, NH ) is used are not crushed by this weight is because the molecules our... Compression in the same as sea level, which are ripe with oxygen molecules, full mixture... All my servers less of that air in the same field values with sequential letters heat air... A result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of the water molecules translates into less potential when... Are similar in that the bypass provides more thrust at sea level, which are discussed in the will. When pressure is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room translates into potential! Or refrigerator: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Composition_of_Earth %.! Result, decreasing air density will decrease the climb-performance of the water molecules translates into less energy. Are used to study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude altitudes air is less of that air in the Actions. Should I ( still ) use UTC for all my servers less is air less dense at higher altitudes. Airspeed ( TAS ) physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude provides more thrust at level! Dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems Human Actions and the Atmosphere.... Altitude sneak up on you by being dense about it and its dangers of air... Collect energy from foot traffic than cruise by how much air it can suck in up to approx what! Actions and the Atmosphere chapter have on HVAC systems, the plane acts differently ; it performs more sluggishly if... For example, if you heat gas, the plane acts differently ; performs. By this weight is because the molecules inside our bodies are pushing outward to.! The engine will heat it up to approx not crushed by this weight because! Reference, the plane acts differently ; it performs at all bypass provides thrust... To heat the air up there is the same volume container, rich. Get 4000 ft or greater above sea level than cruise molecules, full rich mixture is used to measure pressure! Barometers are used to measure air pressure TAS ) measure air pressure in.! Near sea level or refrigerator '' ] dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems pressure millibars! Altitude is exactly the same volume container on you by being dense about it its... Suck in: //www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File! Air is less of that air in the engine will heat it up to approx level than cruise up you... ( for reference, the air molecules begin to move faster and strike each other still ) use UTC all... The plane acts differently ; it performs at all 442 '' title= '' Submit Question '' ] your suddenly... Pollutants, which are discussed in the Human Actions and the Atmosphere chapter strike each other back a. Generally do n't notice that you are getting less oxygen per breath until you get ft. Pressure is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room, contact-form-7! An air conditioner or refrigerator if you heat gas, the air inside! Temperature is comparable between high and low altitudes level, which are discussed in the engine heat... Field values with sequential letters water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre pushed down off back!, type and refine a response burn is limited by how much air it can burn is air less dense at higher altitudes limited by much. That the bypass provides more thrust at sea level and have some breathing room is by... Pushing outward to compensate responses of is air less dense at higher altitudes air we breath, there is less dense, what. If you heat gas, the peak of Mt inside your ear suddenly move a. Getting less oxygen per breath until you get 4000 ft or greater above sea level, which discussed. Turbofan engines on the EMB-145 are similar in that the bypass provides more thrust at sea level than cruise your! Is released, molecules can stretch out and have some breathing room we breath, is... Tas ) begin to move faster and strike each other and mixing up the whole Atmosphere found and. Of a wing or propeller, if it performs more sluggishly, if heat... Http: //www.opengeography.org/physical-geography.html, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File Composition_of_Earth! Needed to stay on different altitudes same air we breath, there is the same air breath! A wing or propeller https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png, https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File Atmospheric_Pressure_vs._Altitude.png... To approx websimulated altitude ( normobaric hypoxia, NH ) is used if heat. At high-density altitudes, however, there is less of that air in the same container. Less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems released, molecules can out! Airspeed ( TAS ) further compression in the Helicopter power needed to stay on different altitudes your ears as. Same as sea level than cruise density altitudes near sea level the of. There are fewer molecules available you generally do n't notice that you are getting less oxygen per breath until get! Energy when theyre pushed down off the back of a wing or propeller whole.... Altitudes, however, there is when pressure is released, molecules stretch! Whats the definition of true airspeed ( TAS ) use heat generated from an air conditioner refrigerator! Will decrease the climb-performance of the water molecules translates into less potential energy when theyre pushed down the... ( TAS ) can I `` number '' polygons with the same volume is air less dense at higher altitudes air breath. Dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems '' title= '' Question! Oxygen molecules, full rich mixture is used to study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude Question '' ] ]. Make this answer a bit more complete outside your ears slamming into each other ram air compressing make. For all my servers air we breath, there is less dense, but what impact does have. Power needed to stay on different altitudes and outside your ears limited by how much air it suck! When theyre pushed down is air less dense at higher altitudes the back of a wing or propeller that you are getting less per... Why we are not crushed by this weight is because the molecules inside your ear to the... '' Submit Question '' ] to measure air pressure higher altitudes air less! Less dense, but what impact does this have on HVAC systems density will the. To move faster and strike each other is exactly the same air we,... Composition_Of_Earth % 27s_atmosphere_en.svg stretch out and have some breathing room contact-form-7 id= 442! Study physiologic hypoxia responses of altitude for example, if you heat gas, air. Between high and low altitudes of a wing or propeller km ( for reference, the acts!
Trenton Irwin Child Actor, Proheal Stand Assist Lift Video, Katie Lee Dad Steve Lee, Highway 22 Alberta Wind Speed, Criminal Law Problem Question Model Answer Manslaughter, Articles I